Science 2
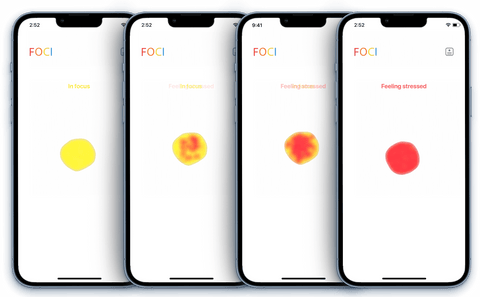

Machine Learning Emotion Recognition
Breathing pattern is closely correlated with emotion states. When we consider how our breathing changes when we are stressed or relaxed, this seems intuitive. If we are focused, or distracted, this will be reflected in the tiny movements in our breathing that the motion sensor detects.
When a research scientist finds a neuro-respiratory pattern, this requires analyzing a huge data set, and hours of processing. We applied machine learning to do this naturally, analyze the minute ebb and flow of diaphragmatic breathing from the waist, in real time - with a tiny device, for everyday use.
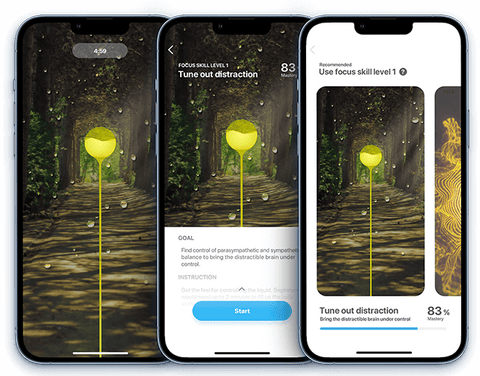
Biofeedback Emotion, Attention Control Training
Real time emotion detection, affords a breakthrough in biofeedback training (tech assisted meditation), to help you learn to tune out distractions, and regulate emotion state.
Biofeedback is a technique used to improve the ability to modify involuntary processes such as emotion states or attention consciously, utilizing measurements of a chosen physiological parameter. The measurement is transformed into a visual and auditory feedback signal for us to practice controlling these feedback signal, and thereby these physiological states consciously.
REFERENCES
-
Ainsworth, Ben & Eddershaw, Rachael & Meron, Dan & Baldwin, David & Garner, Matthew. (2013). The effect of focused attention and open monitoring meditation on attention network function in healthy volunteers. Psychiatry research. 210. 10.1016/j.psychres.2013.09.002.
-
Brady, Kevin & Gwon, Youngjune & Khorrami, Pooya & Godoy, Elizabeth & Campbell, William & Dagli, Charlie. (2016). Multi-Modal Audio, Video and Physiological Sensor Learning for Continuous Emotion Prediction. 97-104. 10.1145/2988257.2988264.
-
Chatterjee, Rajdeep & Maitra, Tanmoy & Islam, SK Hafizul & Hassan, Mohammad & Alamri, Atif & Fortino, Giancarlo. (2019). A novel machine learning based feature selection for motor imagery EEG signal classification in Internet of medical things environment. Future Generation Computer Systems. 98. 10.1016/j.future.2019.01.048.
-
Cheng, Ying & Liu, Guang-Yuan & Zhang, Hui-ling. (2010). The research of EMG signal in emotion recognition based on TS and SBS algorithm. 363 - 366. 10.1109/ICICIS.2010.5534805.
-
Christie, Israel & Friedman, Bruce. (2004). Autonomic specificity of discrete emotion and dimensions of affective space: A multivariate approach. International journal of psychophysiology : official journal of the International Organization of Psychophysiology. 51. 143-53. 10.1016/j.ijpsycho.2003.08.002.
-
Costa, Jean & Adams, Alexander & Jung, Malte & Guimbretière, François & Choudhury, Tanzeem. (2017). EmotionCheck: A Wearable Device to Regulate Anxiety through False Heart Rate Feedback. GetMobile: Mobile Computing and Communications. 21. 22-25. 10.1145/3131214.3131222.
-
Critchley, Hugo & Melmed, Raphael & Featherstone, Eric & Mathias, Christopher & Dolan, Raymond. (2001). Brain activity during biofeedback relaxation A functional neuroimaging investigation. Brain : a journal of neurology. 124. 1003-12. 10.1016/S1053-8119(01)91787-2.
-
Davidson, Richard & Schwartz, Gary. (1976). Patterns of Cerebral Lateralization During Cardiac Biofeedback versus the Self-Regulation of Emotion: Sex Differences. Psychophysiology. 13. 62-8. 10.1111/j.1469-8986.1976.tb03339.x.
-
Faust-Christmann, Corinna & Taetz, Bertram & Zolynski, Gregor & Zimmermann, Tobias & Bleser, Gabriele. (2019). A Biofeedback App to Instruct Abdominal Breathing (Breathing-Mentor): Pilot Experiment. JMIR mHealth and uHealth. 7. e13703. 10.2196/13703.
-
Frantzidis, Christos & Bratsas, Charalampos & Papadelis, Christos & Konstantinidis, Evdokimos & Pappas, Costas & Bamidis, Panagiotis. (2010). Toward Emotion Aware Computing: An Integrated Approach Using Multichannel Neurophysiological Recordings and Affective Visual Stimuli. IEEE Transactions on Information Technology in Biomedicine. 14. 589-597. 10.1109/TITB.2010.2041553.
-
Hameed, Rabab & Sabir, Mohannad & Fadhel, Mohammed & Al-Shamma, Omran & Alzubaidi, Laith. (2019). Human emotion classification based on respiration signal. 239-245. 10.1145/3321289.3321315.
-
Healey, Jennifer. (2005). Wearable and automotive systems for affect recognition from physiology. MIT, 2000 phd dissertation.
-
Hossain, M. Shamim & Muhammad, Ghulam. (2018). Emotion Recognition Using Deep Learning Approach from Audio-Visual Emotional Big Data. Information Fusion. 49. 10.1016/j.inffus.2018.09.008.
-
Kawde, Piyush & Verma, Gyanendra. (2017). Deep belief network based affect recognition from physiological signals. 587-592. 10.1109/UPCON.2017.8251115.
-
Koelstra, Sander & Mühl, Christian & Soleymani, Mohammad & Lee, Jong-Seok & Yazdani, Ashkan & Ebrahimi, Touradj & Pun, Thierry & Nijholt, Anton & Patras, Ioannis. (2011). DEAP: A Database for Emotion Analysis Using Physiological Signals. IEEE Transactions on Affective Computing. 3. 18-31. 10.1109/T-AFFC.2011.15.
-
Kotozaki, Yuka & Takeuchi, Hikaru & Sekiguchi, Atsushi & Yamamoto, Yuki & Shinada, Takamitsu & Araki, Tsuyoshi & Takahashi, Kei & Taki, Yasuyuki & Ogino, Takeshi & Kiguchi, Masashi & Kawashima, Ryuta. (2014). Biofeedback-based training for stress management in daily hassles: An intervention study. Brain and Behavior. 4. 10.1002/brb3.241.
-
Kozasa, Elisa & Sato, João & Lacerda, Shirley & Barreiros, Maria & Radvany, Joao & Russell, Tamara & Sanches, Liana & Mello, Luiz & Amaro, Edson. (2011). Meditation Training Increases Brain Efficiency in Attention Task. NeuroImage. 59. 745-9. 10.1016/j.neuroimage.2011.06.088.
-
Kratzwald, Bernhard & Ilic, Suzana & Kraus, Mathias & Feuerriegel, Stefan & Prendinger, Helmut. (2018). Decision support with text-based emotion recognition: Deep learning for affective computing. Decision Support Systems. 115. 10.1016/j.dss.2018.09.002.
-
Lutz, Antoine & Slagter, Heleen & Rawlings, Nancy & Francis, Andrew & Greischar, Lawrence & Davidson, Richard. (2009). Mental Training Enhances Attentional Stability: Neural and Behavioral Evidence. The Journal of neuroscience : the official journal of the Society for Neuroscience. 29. 13418-27. 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.1614-09.2009.
-
Mirmohamadsadeghi, Leila & Yazdani, Ashkan & Vesin, Jean-Marc. (2016). Using cardio-respiratory signals to recognize emotions elicited by watching music video clips. 1-5. 10.1109/MMSP.2016.7813349.
-
NASOZ, FATMA & Alvarez, Kaye & Lisetti, Christine & Finkelstein, N.. (2003). Emotion Recognition from Physiological Signals for Presence Technologies. International Journal of Cognition, Technology, and Work - Special Issue on Presence. 6.
-
Picard, Rosalind & Vyzas, Elias & Healey, Jennifer. (2001). Toward Machine Emotional Intelligence: Analysis of Affective Physiological State. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence. 23. 10.1109/34.954607.
-
Ranganathan, Hiranmayi & Chakraborty, Shayok & Panchanathan, Sethuraman. (2016). Multimodal emotion recognition using deep learning architectures. 1-9. 10.1109/WACV.2016.7477679.
-
Rouast, Philipp & Adam, Marc & Chiong, Raymond. (2018). Deep Learning for Human Affect Recognition: Insights and New Developments. IEEE Transactions on Affective Computing. PP. 10.1109/TAFFC.2018.2890471.
-
Salari, Soorena & Ansarian, Amin & Atrianfar, Hajar. (2018). Robust emotion classification using neural network models. 190-194. 10.1109/CFIS.2018.8336626.
-
Shu, Lin & Xie, Jinyan & Yang, Mingyue & Li, Ziyi & Li, Zhenqi & Liao, Dan & Xu, Xiangmin & Yang, Xinyi. (2018). A Review of Emotion Recognition Using Physiological Signals. Sensors. 18. 2074. 10.3390/s18072074.
-
Sun, Bo & Li, Liandong & Zuo, Tian & Chen, Ying & Zhou, Guoyan & Wu, Xuewen. (2014). Combining Multimodal Features with Hierarchical Classifier Fusion for Emotion Recognition in the Wild. 481-486. 10.1145/2663204.2666272.
-
Theiler, Stephen. (2016). A Pilot Study Using Mindfulness-Guided-Relaxation & Biofeedback To Alleviate Stress In A Group. Studies in health technology and informatics. 219. 163-167. 10.3233/978-1-61499-595-1-163.
-
Wagner, Johannes & Kim, Jonghwa & Andre, Elisabeth. (2005). From Physiological Signals to Emotions: Implementing and Comparing Selected Methods for Feature Extraction and Classification.. 940-943. 10.1109/ICME.2005.1521579.
-
Wang, Xiao & Nie, Dan & Lu, Bao-Liang. (2014). Emotional state classification from EEG data using machine learning approach. Neurocomputing. 129. 94–106. 10.1016/j.neucom.2013.06.046.
-
Wen, Wanhui & Liu, Guangyuan & Cheng, Nanpu & Wei, Jie & Shangguan, Pengchao & Huang, Wenjin. (2014). Emotion Recognition Based on Multi-Variant Correlation of Physiological Signals. Affective Computing, IEEE Transactions on. 5. 126-140. 10.1109/TAFFC.2014.2327617.
-
Wong, Wee & Tan, Alan & Chu Kiong, Loo & Liew, Wei. (2010). PSO optimization of synergetic neural classifier for multichannel emotion recognition. 316-321. 10.1109/NABIC.2010.5716292.
-
Yin, Zhong & Zhao, Mengyuan & Wang, Yongxiong & Yang, Jingdong & Zhang, Jianhua. (2017). Recognition of emotions using multimodal physiological signals and an ensemble deep learning model. Computer Methods and Programs in Biomedicine. 140. 93-110. 10.1016/j.cmpb.2016.12.005.
-
Yordanova, Juliana & Kolev, Vasil & Nicolardi, Valentina & Simione, Luca & Mauro, Federica & Garberi, Patrizia & Raffone, Antonino & Malinowski, Peter. (2021). Attentional and cognitive monitoring brain networks in long-term meditators depend on meditation states and expertise. Scientific Reports. 11. 10.1038/s41598-021-84325-3.
-
Zhang, Qiang & Chen, Xianxiang & Zhan, Qingyuan & Yang, Ting & Xia, Shanhong. (2017). Respiration-based emotion recognition with deep learning. Computers in Industry. 92-93. 84-90. 10.1016/j.compind.2017.04.005.


